Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a narrow passageway surrounded by bones and ligaments on the palm side of the hand, compressing the median nerve. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers. Osteopathy can help alleviate symptoms of CTS through various techniques such as manual therapy, acupuncture, shockwave therapy as well as a holistic approach considering the whole body, and lifestyle factors.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Repetitive Motion: Activities that involve repetitive wrist movements, such as typing, using a mouse, or assembly line work.
- Anatomical Factors: Smaller carpal tunnels can predispose individuals to CTS.
- Medical Conditions: diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disorders can increase the risk.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes can lead to fluid retention, which may increase pressure within the carpal tunnel.
- Injuries: Wrist fractures or dislocations can alter the space within the carpal tunnel.
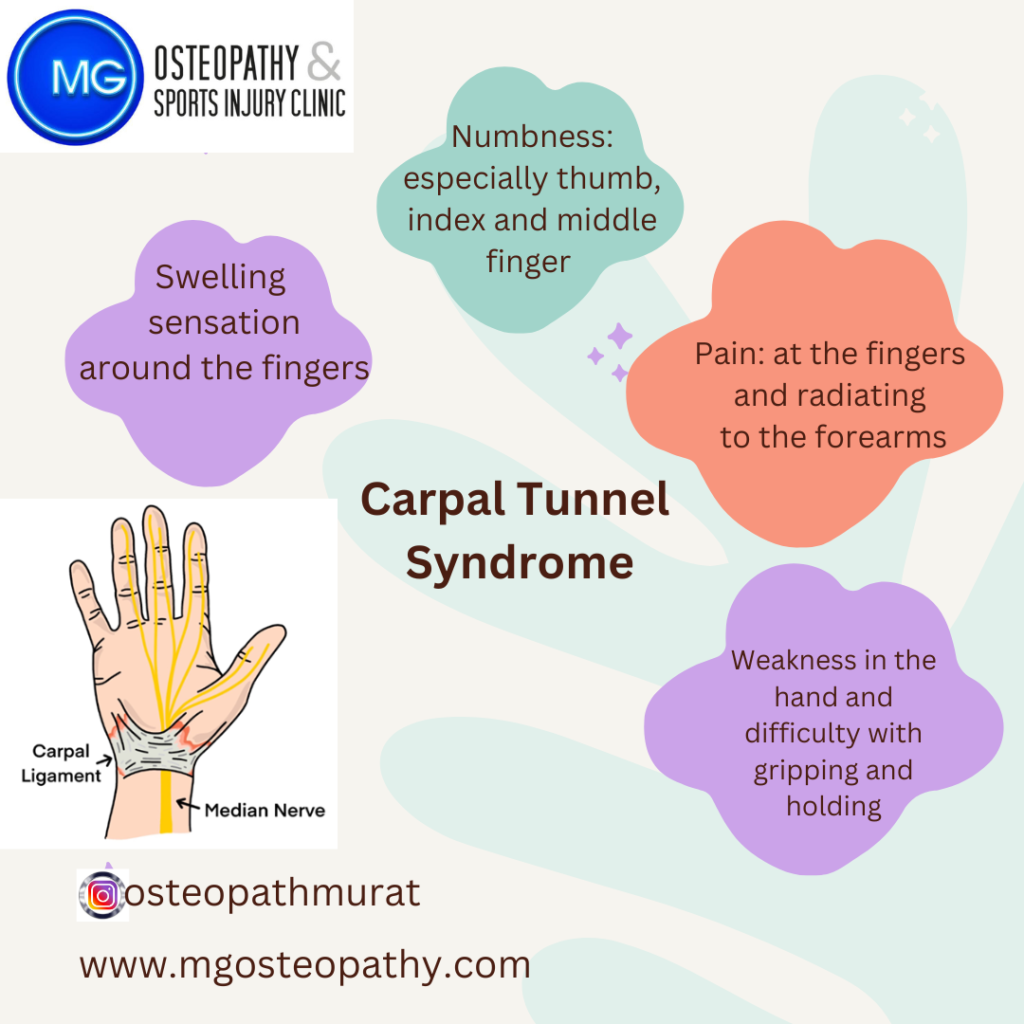
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Numbness and Tingling: Often felt in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring fingers.
- Pain: Pain that may radiate up the arm or be concentrated in the wrist and hand.
- Weakness: Decreased grip strength, making it difficult to hold objects.
- Clumsiness: Tendency to drop things due to a loss of proprioception.
Holistic Osteopathic Approach to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Manual Therapies:
- Soft Tissue Manipulation: Gentle massage and stretching of muscles and fascia in the hand, wrist, forearm, and upper limb to reduce tension and improve circulation.
- Myofascial Release: Focus on releasing tightness in the fascia to improve mobility and reduce nerve compression.
- Joint Mobilization: Gentle movements to enhance joint function and decrease stiffness in the wrist and surrounding areas.
- Nerve Gliding Exercises: Specific exercises to help the median nerve move freely within the carpal tunnel, reducing irritation.
- Ergonomic and Postural Adjustments:
- Workstation Ergonomics: Adjust your workstation setup, including keyboard, mouse, and chair positioning, to reduce wrist strain.
- Postural Training: Teach proper posture and body mechanics to avoid undue stress on the wrists during daily activities.
- Exercise and Stretching Programs:
- Strengthening Exercises: Target the muscles of the hand, wrist, and forearm to improve overall function and support.
- Stretching Exercises: Focus on stretching the wrist flexors and extensors to maintain flexibility.
- General Physical Activity: Encourage regular, overall physical activity to improve circulation and general health.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Activity Modification: Identify and modify activities that exacerbate symptoms, ensuring regular breaks to rest the wrists.
- Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to reduce overall muscle tension.
- Nutritional Support:
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Encourage a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids) and low in processed foods and sugars.
- Hydration: Emphasize the importance of staying hydrated to support overall tissue health.
- Adjunct Therapies:
- Acupuncture: May be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Shockwave therapy: could be used for pain relief and enhance healing
- Education and Self-Care:
- Patient Education: Teach about the condition, its causes, and preventive measures.
- Self-Massage Techniques: Instruct on safe self-massage techniques to use at home.
Home Exercises: Provide a regimen of exercises and stretches to perform regularly.